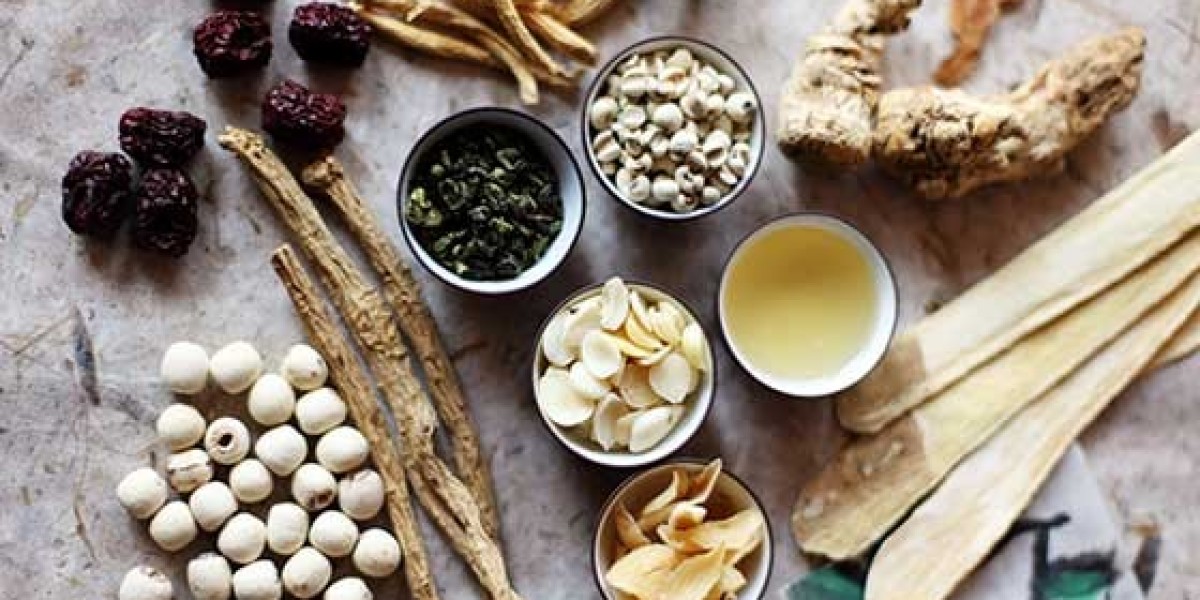
The TCM treatment of diabetes is based on the theory of qi and blood, viscera (five zang organs and six fu organs) and yin and yang (two opposite principles in the body), which is different from western medicine.
According to TCM theory, the common patterns of type 2 diabetes are deficiency of qi and yin (body fluid), heat and blood stasis. Qi deficiency and yin deficiency patterns may occur in the initial stage, leading to tissue heat and blood stasis. Alternatively, heat can occur earlier, or both yin deficiency and heat may occur for a relatively longer duration, while stasis can occur at any stage. Therefore, commonly used traditional Chinese medicine formulas can be divided into four categories: tonifying qi, nourishing yin, clearing heat, and resolving blood stasis. The most commonly used herbs are Huangqi, Dihuang, Zhimu, and Danshen, which belong to the above groups respectively.
In China, government owned medical service institutions are responsible for the treatment of the majority of patients, with an average hospital delivery rate of 95% in 2011. Since the mid-1990s, the growth rate of the private sector has surpassed that of the public sector, especially in rural areas. Diabetes in china is mainly managed in the public health care sector as an inpatient or outpatient service.
Traditional Chinese medicine has its own pathogenesis theory, diagnostic techniques, and treatment principles. Generally speaking, diseases are considered to be the interaction of internal and external factors, leading to disorders of qi and blood, internal organs, and yin yang imbalance. The diagnostic system of traditional Chinese medicine consists of four types of examinations: examination, hearing/smelling, inquiry, and palpation. Tongue examination and pulse examination are two unique diagnostic methods in traditional Chinese medicine compared to Western medicine. Treatment is based on syndrome differentiation. Syndrome differentiation is a method of diagnosis based on the theory of traditional Chinese medicine, which comprehensively analyzes the data of the four syndromes. The main methods of syndrome differentiation include: syndrome differentiation based on eight principles, etiology, qi, blood, body fluid, viscera, six meridians, Wei Qi and Yang Blood, and San Shao. The treatment philosophy and goal of traditional Chinese medicine is to focus on the overall functional status of patients, which is different from Western medicine. Acupuncture and moxibustion, Chinese herbal medicine (chinese herb medicine store), Chinese die to therapy, Chinese exercise therapy and manual therapy are the five major branches of Chinese medicine.