2-butanol is used to produce methyl ethyl ketone and Sec-Butyl acetate, as the solvent for paint and alkyd enamel, in hydraulic brake fluid, in cleaning compounds, and in flotation of its xanthate derivatives.
Under dehydration catalyst, butanol can generate butene, n-butanol and 2-butene can generate 1-Butene, 2-butene and 2-butanol can generate 2-butene, and Isobutanol and Tert-Butyl alcohol can generate isobutene. Under the catalysis of copper and silver, dehydrogenation generates carbonyl compounds, n-butanol generates butyraldehyde, butanol generates methyl ethyl ketone, and Isobutanol generates Isobutyraldehyde. Under the action of a catalyst, air oxidation can generate acids. Under the catalysis of Mineral acid, it reacts with organic acid to form ester. Reacting with benzene can generate butyl benzene. Butanol reacts with chlorine to form butyraldehyde chloride. Under the action of aluminum catalyst, n-butanol, Isobutanol and 2-butanol react with ammonia at 300~350 ℃ to produce butylamine, Dibutylamine and tributylamine, while t-butanol does not have this characteristic. N-butanol and Tert-Butyl alcohol react with hydrogen sulfide at 180 ℃ to produce butyl mercaptan.
There are two methods for producing 2-butanol in industry. The first method is butene hydration. After pretreatment, n-butene is hydrated with sulfuric acid to obtain 2-butanol, which is purified to obtain 2-butanol. The second is the ion exchange resin hydration method, which uses n-butene as the raw material and acidic cation exchange resin as the catalyst to undergo liquid-phase esterification reaction with organic acids, and then hydrolyze and distill to obtain the product.
Exposure to 2-butanol may cause eye and skin irritation. The latter effect is produced by its degreasing effect on the skin. The toxicity of butanol isomers is relatively mild, similar to other butanol isomers. High concentrations can cause anesthesia. The anesthetic effect is stronger than that of n-butanol, which may be due to the higher Vapor pressure of secondary alcohol.
Its toxicity is lower than its original alcohol analogues.
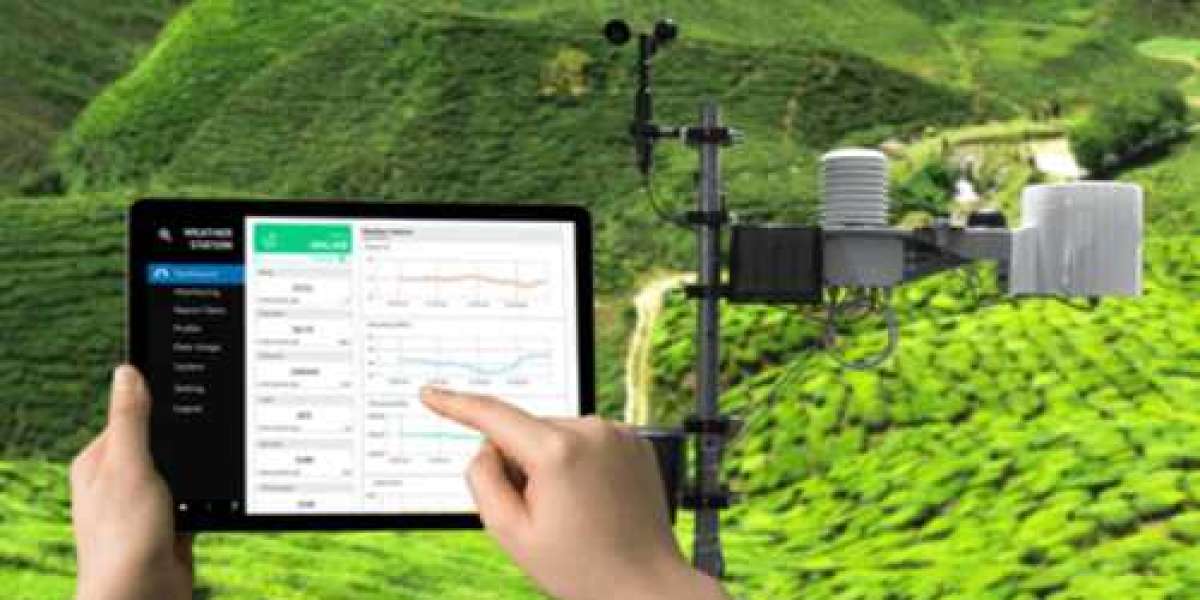
2 butanol is widely used as a solvent for cleaning agents and paint removers. It is also used in perfume and artificial perfumes. It plays an important role in extracting fish meal to produce protamine. It is involved in the production of fruit essence. It plays an important role in the esterification reaction of acetic acid. It can be used for the derivatization of hydroxyfuranone chloride. It is also used as a precursor for methyl ethyl ketone.
The type of Intermolecular force in 2-butanol is hydrogen bond, which is caused by the direct connection of Electronegativity atoms such as oxygen (O) with protons.
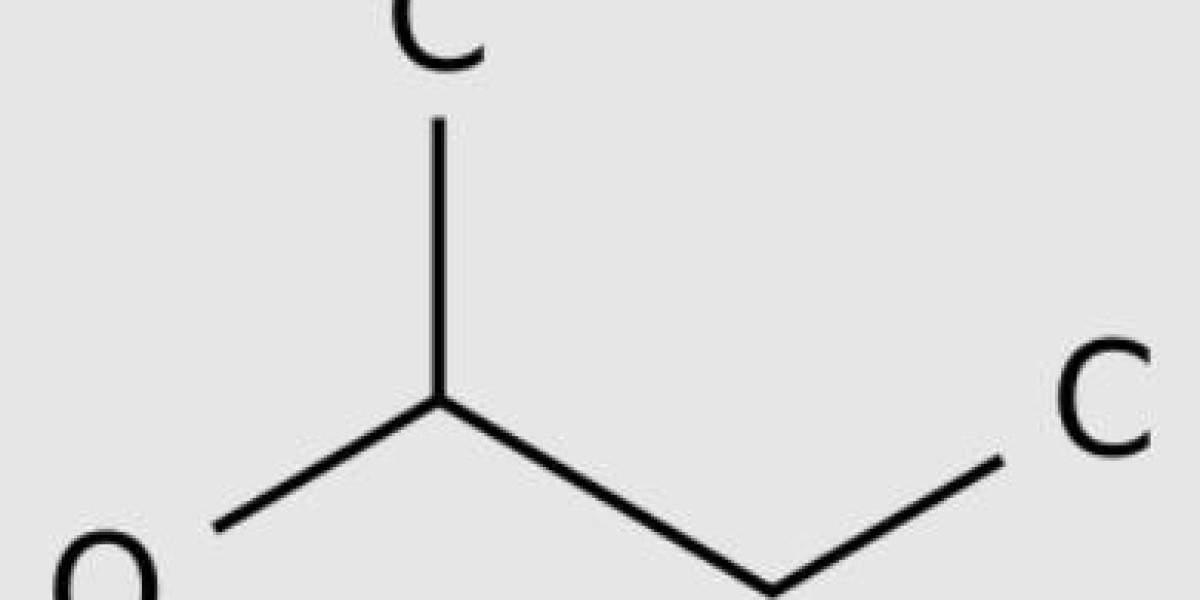
Butanol is an alcohol. It is an organic compound with a functional group - OH connected to carbon atoms. Butanol has four carbon atoms. The general formula for butanol is C4H9OH. This Molecular formula has five isomers. Isomers are molecules with the same Molecular formula but different chemical structures. 1-butanol and 2-butanol are two isomers. The main difference between No.1 butanol and No.2 butanol is that the - OH group of No.1 butanol is connected to the carbon at the molecular end, while the - OH group of No.2 butanol is connected to the second carbon atom.