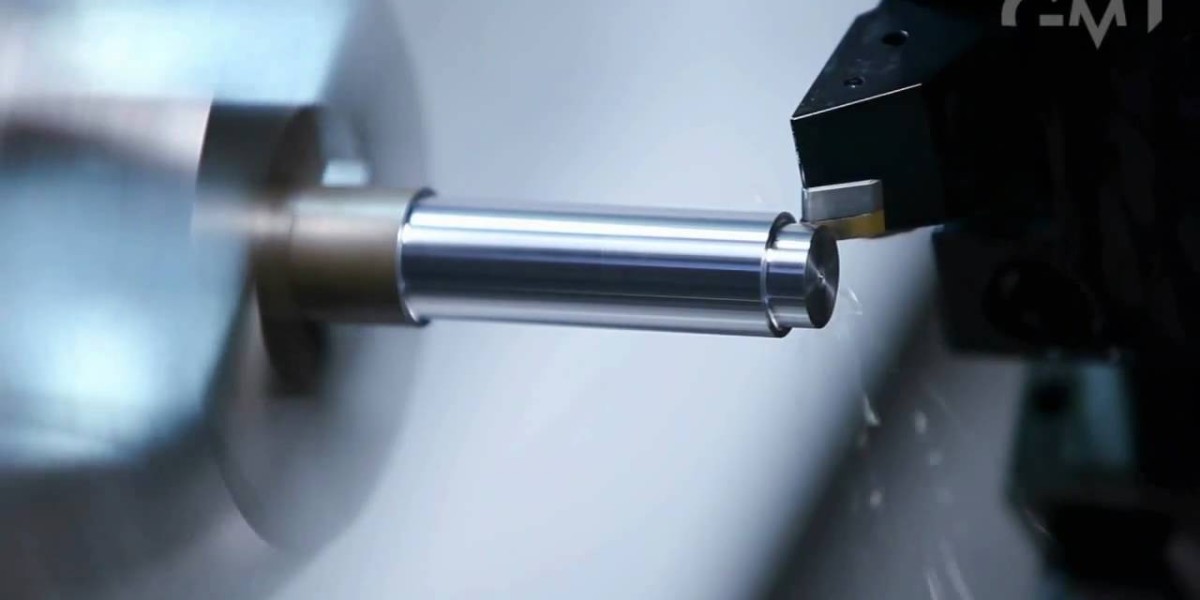
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) turning is a subtractive manufacturing technique that utilizes automated machines to shape raw material into complex and intricate components. This article explores the intricacies of CNC Turning Parts, shedding light on their manufacturing process, applications, advantages, and the future of this remarkable technology.
- Understanding CNC Turning:
CNC turning is a machining process that involves the rotation of a workpiece while a cutting tool removes material to create the desired shape. The turning machine, controlled by a computer program, precisely positions the cutting tool to achieve high levels of accuracy and repeatability. This process is ideal for creating cylindrical or conical shapes, such as shafts, bushings, and connectors, among others.
- Manufacturing Process of CNC Turning Parts:
a. Material Selection: CNC turning parts can be manufactured from a wide range of materials, including metals like aluminum, steel, brass, and titanium, as well as various plastics and composites. Material selection depends on factors such as the intended application, strength requirements, and cost considerations.
b. CAD Design: The first step in creating CNC turning parts is designing the component using computer-aided design (CAD) software. The design specifies the dimensions, tolerances, and surface finishes required for the part.
c. CAM Programming: Once the CAD design is complete, the next step is to generate a CNC program using computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software. This program provides instructions to the CNC machine on tool paths, cutting speeds, feed rates, and other parameters necessary to manufacture the part accurately.
d. Machine Setup: The CNC turning machine is prepared for the manufacturing process by installing the workpiece, aligning the cutting tool, and configuring the machine's settings according to the programmed instructions.
e. Turning Process: The CNC machine rotates the workpiece at high speeds while the cutting tool removes material in precise increments. The cutting tool may move along multiple axes to create complex shapes and features, such as threads, chamfers, and grooves.
f. Quality Control: Throughout the manufacturing process, quality control measures ensure that the CNC turning parts meet the required specifications. This may involve dimensional inspections using precision measuring tools and surface analysis techniques to ensure a flawless finish.
g. Finishing Operations: After the turning process, additional finishing operations may be carried out, such as deburring, polishing, or coating, to improve the part's aesthetics, functionality, and durability.
- Applications of CNC Turning Parts:
CNC turning parts find applications in numerous industries, including:
a. Automotive: CNC turning parts are widely used in the automotive industry to manufacture engine components, transmission parts, suspension components, and various precision fittings.
b. Aerospace: The aerospace industry relies heavily on CNC turning parts to produce critical components such as turbine shafts, aircraft landing gears, hydraulic connectors, and structural elements.
c. Electronics: CNC turning parts are essential in the electronics industry for creating connectors, terminals, and housings for electronic devices.
d. Medical: CNC turning parts play a vital role in medical device manufacturing, producing components such as surgical instruments, implants, and diagnostic equipment.
e. Industrial Machinery: CNC turning parts are utilized in the production of industrial machinery, including pumps, valves, gears, and drive shafts.
- Advantages of CNC Turning Parts:
a. High Precision: CNC turning offers exceptional precision and repeatability, ensuring tight tolerances and accurate dimensions, even for complex geometries.
b. Versatility: CNC turning machines can work with a wide range of materials, enabling the production of diverse components for various industries.
c. Efficiency and Speed: CNC turning parts can be manufactured efficiently, reducing production times and costs compared to traditional machining methods.
d. Automation: The automated nature of CNC turning minimizes the need for manual intervention, reducing human error and increasing productivity.
e. Scalability: CNC turning allows for easy scalability, enabling manufacturers to produce small batches or large volumes of parts based on demand.
- The Future of CNC Turning Parts:
As technology continues to advance, the future of CNC turning parts looks promising. Some notable developments include:
a. Enhanced Automation: Further advancements in automation and robotics will increase the efficiency and productivity of CNC turning processes.
b. Integration of AI and Machine Learning: AI-powered systems can optimize tool paths, predict machine maintenance needs, and enhance process control, leading to higher precision and reduced downtime.
c. Additive Manufacturing Integration: Combining CNC turning with additive manufacturing techniques can open up new possibilities for complex part designs and improved material properties.
d. IoT Connectivity: Integration with the Internet of Things (IoT) will enable real-time monitoring and remote control of CNC turning machines, enhancing process control and overall productivity.
Conclusion:
CNC turning parts are at the forefront of precision engineering, delivering intricate components with exceptional accuracy and efficiency. From the initial design stage to the final finishing operations, CNC turning offers numerous advantages in terms of precision, versatility, and scalability. With ongoing advancements in automation, AI integration, and additive manufacturing, the future of CNC turning parts holds exciting possibilities for innovation and improved manufacturing processes across industries.