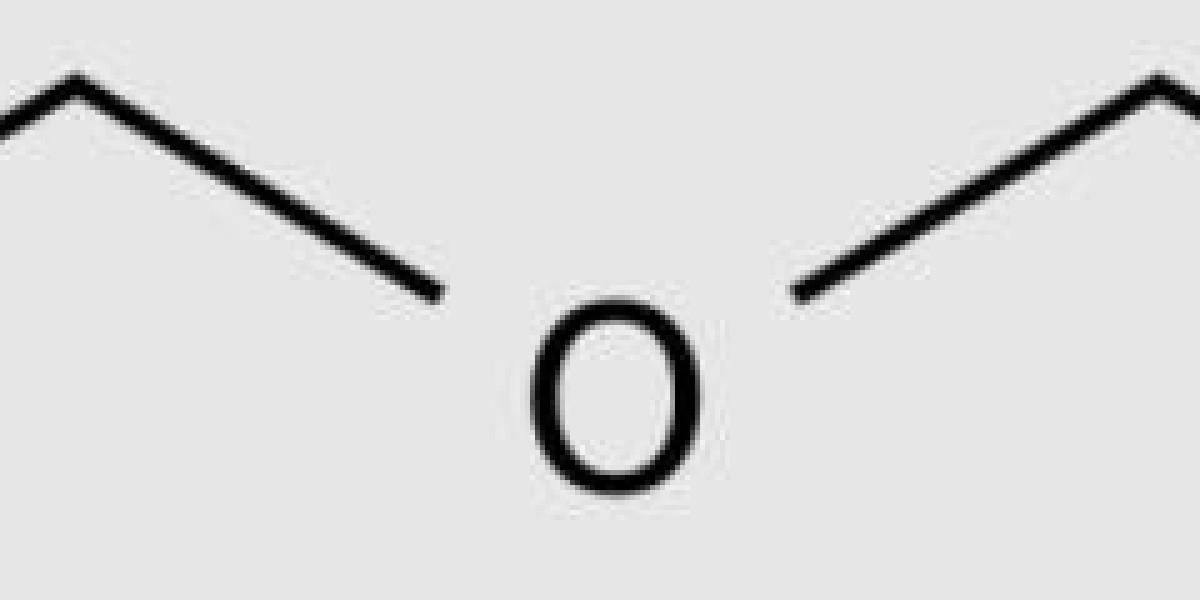
Diethyl ether is the most important species in the Diethyl ether family. It is usually abbreviated as Ether. c2 h50c2 h5
Laboratory preparation: In the laboratory, excessive ethanol is heated with conc to prepare ether. 413k sulfuric acid.
Physical properties of diethyl ether
Diethyl ether is a colorless and highly volatile liquid. The boiling point is 308k. It is lighter than water.
It has a pleasant odor and a burning smell. Inhaling its vapor can cause people to lose consciousness.
Slightly soluble in water, easily miscible with alcohol, benzene, etc.
definition
The use of diethyl ether
It is mainly used as a solvent for oils, fats, gums, resins, plastics, etc.
Used as a refrigerant.
It is used as a general anesthetic in surgical procedures.
After mixing with alcohol, it is called Natalite as a substitute for gasoline.
Diethyl Diethyl ether (CAS 60-29-7) is a component of the starting fluid used as a solvent in the manufacture of synthetic dyes and plastics. Due to its characteristics, Diethyl ether was widely used as an anesthetic in many countries, but was replaced by other substances in the 1960s. The main route of contact is inhalation. The mechanism and site of action of Diethyl ether are still unclear. The effect of Diethyl ether on the central nervous system is mainly achieved through interactions with neuronal membranes and ion channels.
Compared with other anesthetic ethers, Diethyl ether has higher water solubility. Diethyl ether smells sweet and slightly irritating; Although it can be used for inhalation induction, Diethyl ether induction is very slow and risky for laryngeal spasms. Diethyl ether is still used as an anesthetic in some developing countries due to its low cost, high therapeutic index, and minimal inhibition of the heart and respiration. Its flammability has made it no longer used in most developed countries. Diethyl ether is not a cardiac inhibitor and can maintain baroreceptor reflex, making it relatively safe for patients with septic shock. The incidence rate of PONV with Diethyl ether is high.
Diethyl ether is no longer used as a general anesthetic. It is highly flammable and therefore incompatible with modern surgical and anesthesia techniques. It has an unpleasant odor that stimulates the mucous membranes; This can lead to coughing, tension, throat spasms, and excessive saliva secretion. Recovery is slow, with up to 85% of patients experiencing nausea and vomiting. Liver damage is as frequent as halothane. Diethyl ether can increase intracranial pressure and cause convulsions. It can lead to impaired immune response, contact dermatitis has been reported, and is accompanied by systemic allergic reactions.
Diethyl ether may be the most commonly used solvent for extracting clomiphene, for example, extracting clomiphene from 3ml of plasma in 1ml of borate buffer solution with a pH of 9 and an extraction efficiency of 70% at 30ng/mL.