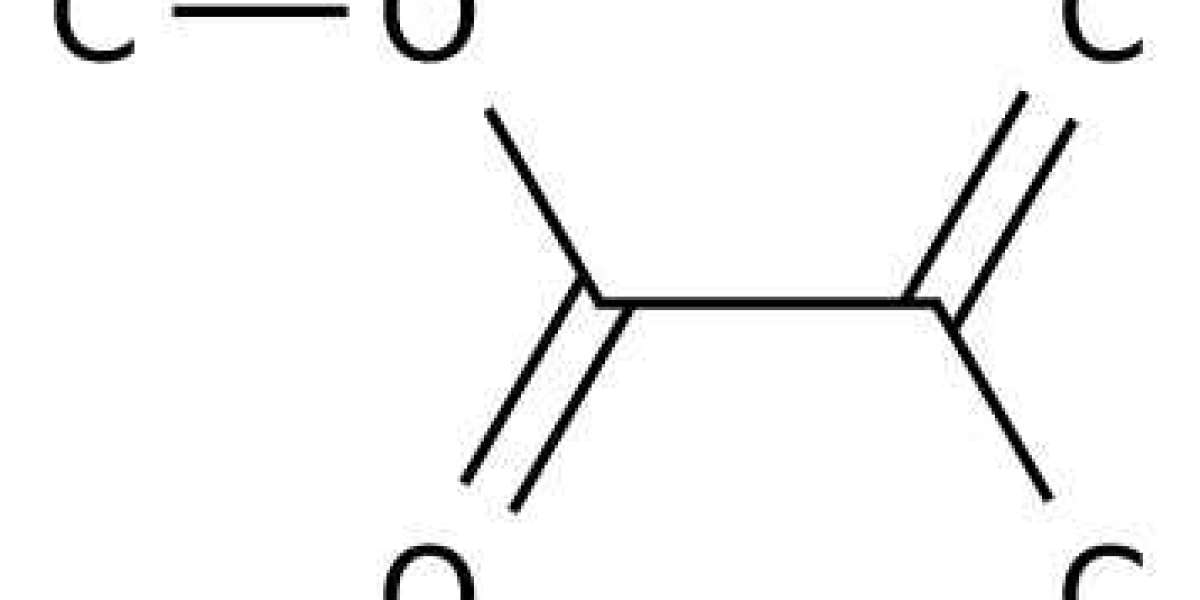
Poly Methyl Methacrylate, or PMMA, is known by many different names, including Plexiglas and acrylic. The biocompatibility of poly methyl methacrylate material has gained it the medical moniker of “bone cement.” Poly methyl methacrylate is often used as a lighter, shatter-resistant alternative to glass in everything from windows, aquariums and hockey rinks. Therefore, it’s hard to fathom that this easy-to-process, low-cost, versatile material is also used in dentures, bone implants and more. Despite being formed by polymerizing methyl methacrylate (MMA) — an irritant and possible carcinogen — poly methyl methacrylate is extremely biocompatible.
As bone cement, poly methyl methacrylate is used to fill in the gaps between implants and bones. Poly methyl methacrylate material is good for this procedure because it is biocompatible and simple to polymerize within a hospital environment. However, a better understanding of material intelligence can help answer whether poly methyl methacrylate is always a good option for in vivo implants.
Though Poly Methyl Methacrylate Material Is Biocompatible, Is It Always the Best Medical Option?
In an operation room, bone cement is made from a powder and a liquid. The powder is composed of MMA copolymers while the liquid contains MMA monomers and chemical accelerators and inhibitors.
Mixing the powder and liquid creates a putty which can be applied between the bone and the implant. Think of the putty like the grout between tiles: It anchors the implant to the bone.
Doctors Benefit from the Biocompatibility of Poly Methyl Methacrylate Material
Poly methyl methacrylate is an important material for many other medical procedures. For instance, it is used to make dentures and fillings because it is easy to dye and quick to form. As a result, doctors can use poly methyl methacrylate material to make dentures and fillings that closely match the size and color of the original teeth. Poly methyl methacrylate material has also made it into the eye. Historically, it was used as hard contacts or intraocular lenses.
Doctors Benefit from the Biocompatibility of Poly Methyl Methacrylate Material
Poly methyl methacrylate is an important material for many other medical procedures. For instance, it is used to make dentures and fillings because it is easy to dye and quick to form. As a result, doctors can use poly methyl methacrylate material to make dentures and fillings that closely match the size and color of the original teeth. Poly methyl methacrylate material has also made it into the eye. Historically, it was used as hard contacts or intraocular lenses.
The ocular use of poly methyl methacrylate started through a surprising discovery. An ophthalmologist working with the Royal Air Force, Sir Harold Ridley, noticed that splinters of poly methyl methacrylate in the eye — resulting from shattering windshields — did not trigger the same rejection as glass splinters.