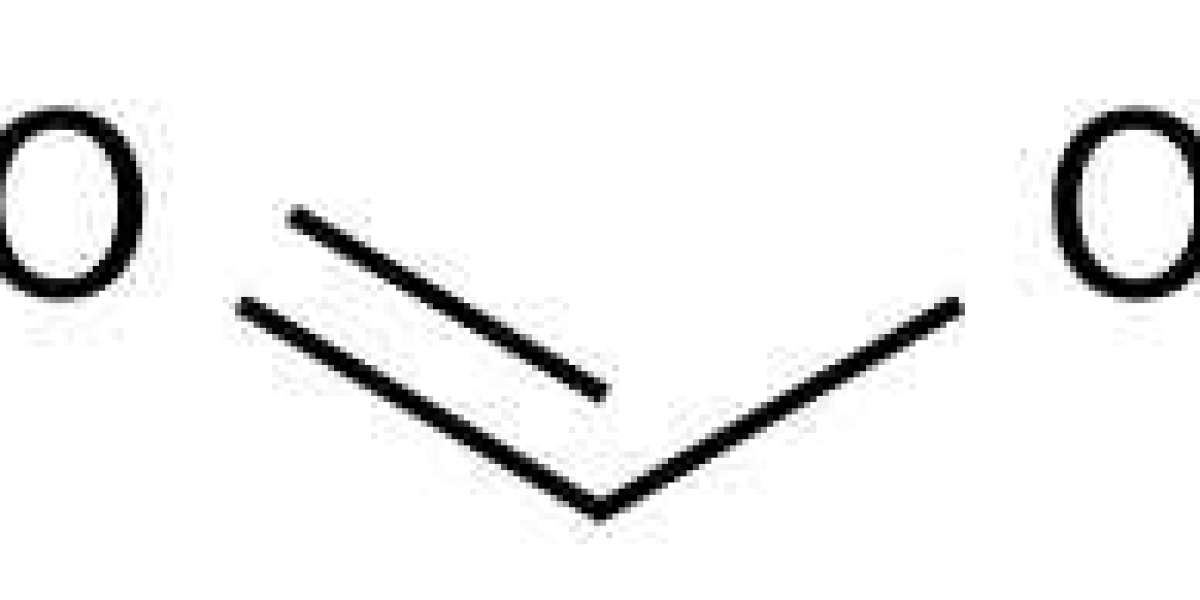
Formic Acid
There are many elements and compounds in nature. Some occur naturally, while others are obtained in laboratories. Today, scientists can produce naturally occurring compounds in laboratories for studies or even in industries for mass production. Formic acid is one of them.
Have you ever been masticated by an ant or bee? Have you felt a tingling sensation when they bite you? It happens due to the venom of bees and ants that enter your body when they bite you. Can you guess what that venom contains? Yes! that’s formic acid. The following article explains formic acid, its manufacturing, properties, and uses to aid students in understanding it more.
Formic Acid Formula
The formic acid formula contains one carbon atom, two oxygen atoms, and two hydrogen atoms. Due to the presence of the carboxyl group, its molecular formula becomes HCOOH. Due to the hydrogen bonding between its two molecules can occur in the form of a dimer.
Acidity Comparison of Acetic Acid and Formic Acid
An acid’s acidity depends on the carboxylate anion’s stability. The more stable the negative charge, the more acidic the acid (equilibrium will lie more on the dissociated side of the equation). Methyl groups (like in acetic acid) are appraised to be electron donating (by hyperconjugation effect) contrasted to a hydrogen substituent (like in formic acid). In the carboxylate anion, stability is gained by the delocalisation of the negative charge if the methyl group is donating electron density, making the carboxylate less stable than the effect of the hydrogen (none, by definition) in formic acid.
Conclusion
Methanoic acid or formic acid is a corrosive liquid, colourless, pungent smell, and is the simplest carboxylic acid. The chemical formic acid formula is H2CO2 or HCOOH. It is a miscible acid that can mix in all proportions with ethanol and water. It is because formic acid can form hydrogen bonding with ethanol or water molecules. In the gaseous form, formic acid does not obey the ideal gas law. The reason is simply the establishment of hydrogen bonding. As compared to other monocarboxylic acids like acetic acid, formic acid is a stronger acid.