According to GlobalData's forthcoming Thematic Research, growth in the non-vaccine mRNA therapeutics landscape by 2028 will be driven by the approval of several pipeline agents: report from mRNA Therapeutics. There are as of now no advertised non-antibody mRNA therapeutics in any of the seven significant business sectors (7MM), which incorporate the US, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, and the UK (5EU), and Japan. In any case, there has been a flood of interest in the mRNA therapeutics space after the Coronavirus pandemic wherein mRNA immunizations demonstrated fruitful.
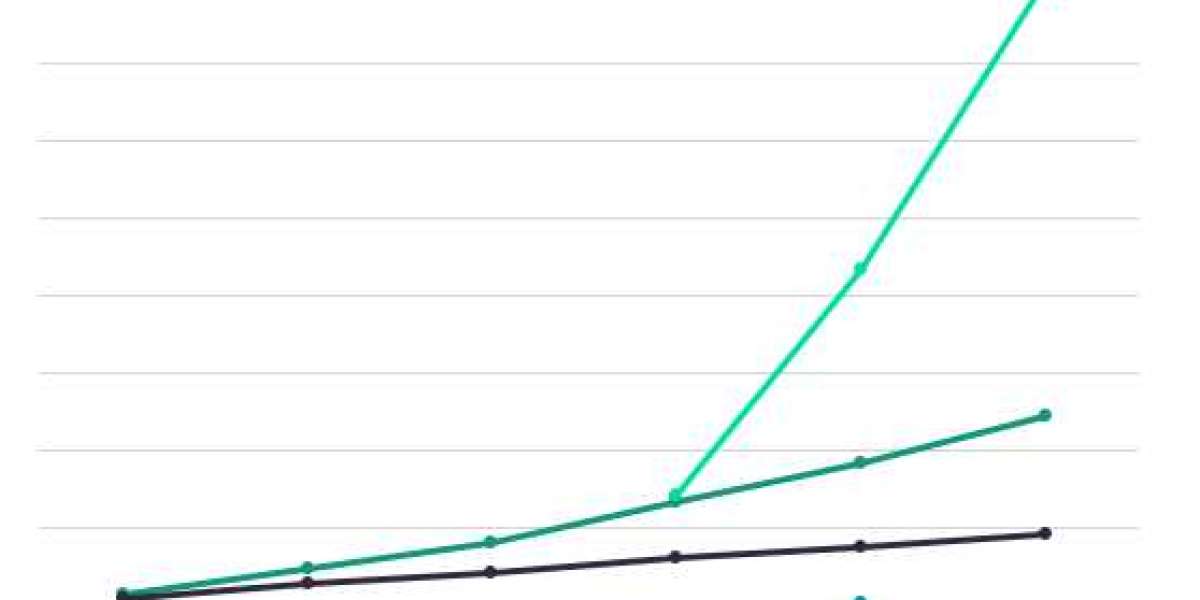
Moderna, Ultragenyx, Omega Therapeutics, and BioNTech are among the pharmaceutical companies currently conducting additional research into mRNA therapeutics for the treatment of cancer and rare genetic diseases. Five non-vaccine mRNA therapies are currently undergoing Phase I/II clinical trials. According to analyst consensus forecasts on GlobalData's Pharma Intelligence Centre, their combined revenue is expected to exceed $2 billion by 2028, with Ultragenyx's OTX-2002 generating $1.6 billion in sales in 2028.
Omega Therapeutics is working on developing OTX-2002 for the treatment of solid tumors and hepatocellular carcinoma. The potential treatment is an epigenomic controller and an inhibitor of the myc proto-oncogene protein. To alter gene expression, the candidate is delivered as mRNA. Moderna is currently working on two mRNA therapies that are not vaccines: mRNA-3705 for propionic acidemia and mRNA-3927 for methylmalonic acidemia, respectively. The anticipated revenue from each of these indications, which are both rare genetic disorders, is $278 million and $491 million, respectively.
Glycogen storage disorder type III, also known as Cori's disease, is yet another uncommon genetic condition under investigation. Through its glycogen debranching enzyme replacement therapy, Ultragenyx's LUNAR-GSD3/UX053 aims to address the tissue accumulation of abnormally structured glycogen in Cori's disease. BioNTech's BNT-141, a claudin18.2 inhibitor, is the final non-vaccine mRNA therapeutic in Phase I/II. The drug candidate elicits anti-tumor activity by inhibiting claudin18.2. For ovarian cancer, bile duct cancer (cholangiocarcinoma), adenocarcinoma of the gastroesophageal junction, colorectal cancer, pancreatic cancer, and solid tumors, BioNTech is developing a pipeline drug.
The following are opportunities in the mRNA therapeutics landscape:
Ability to act on targets that are otherwise "undruggable" for small molecules, relatively high transfection efficiency, and low toxicity given that mRNA does not need to enter the nucleus to be function Barriers within the mRNA therapeutics landscape include: Minimal manufacturing changes for multiple targets Ability to restore gene expression without the risk of genomic integration
Cell Gene Therapy coverage on Clinical Trials Arena is supported by Cytiva. Instability because mRNA is susceptible to degradation by ribonucleases Lipid nanoparticles must be tissue-specific and biodegradable. Risk of activating the immune system. Difficult to achieve high quality and purity of mRNA with scalable manufacturing.
Independently produced, editorial content adheres to the highest standards of journalistic integrity. The creation of editorial content does not involve topic sponsors.