What is Tungsten?
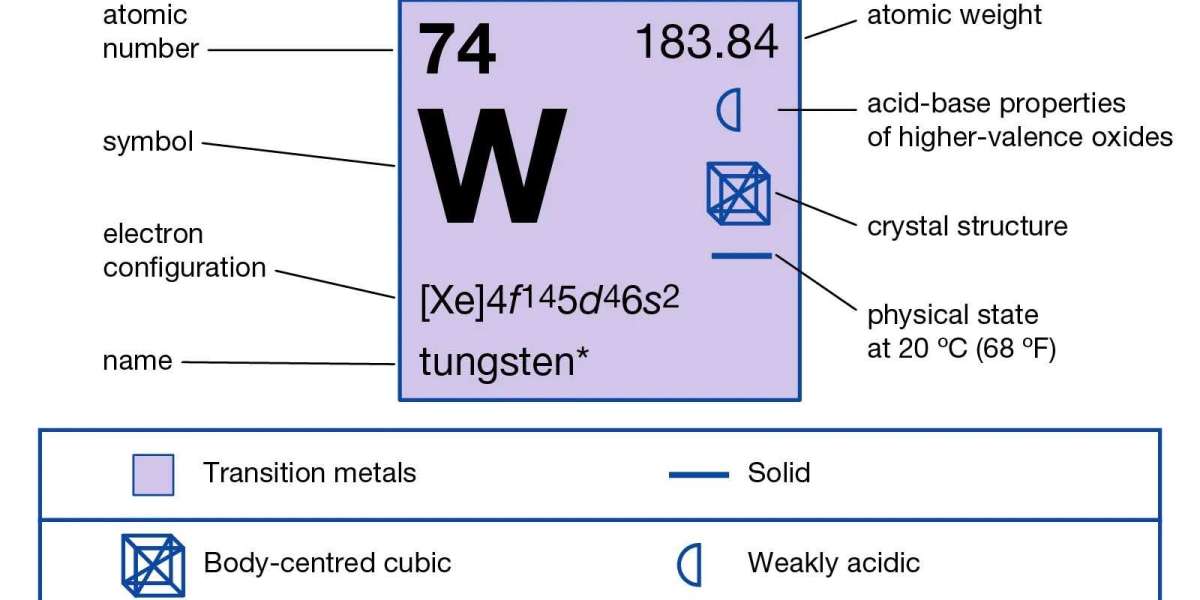
Tungsten is an abundant tin white or steel gray metal that is known to be one of the toughest metals on earth. It has exceptional tensile strength and resistance to high temperatures with a melting point of 6191 °F or 3421.7 °C with a boiling point of 10220 °F or 5660 °C. Tungsten has an atomic number of 74 and is part of the transition metal group on the periodic table.
Occurrence of Tungsten Metal
Tungsten is a naturally occurring element that is found in minerals wolframite and scheelite. Wolframite is an iron manganese tungstate with the chemical composition of (FeMn)WO4 and is a solid solution of the two minerals which are ferberite (FeWO4) and hubnerite MnWO4 and scheelite is calcium tungstate (CaWO4). Some other what is tungsten minerals vary in their level of occurrence and abundance from semi moderate to very rare and have nearly no economic value.
Tungsten is Brittle
Brittle means that it is easily broken down when man handled or put under great stress. Tungsten metal is very easy to fracture when put under stress and therefore it is mixed with other metals to obtain their non brittle characteristics. Mixing tungsten with carbon makes it significantly stronger and allows it to be used in some areas where it would not have been used on its own.
What is Tungsten Chemical Properties
Tungsten is located in the transitional group of the chemistry periodic table and has oxidation states of + 2, + 3, + 4, + 5, and + 6. It has an atomic number of 74 and a relative atomic mass of 183.84. Tungsten is a solid at room temperatures because of a stable isometric crystal formation which can be seen under an x-ray. Tungsten is very resistant to corrosion by acids and is only vulnerable to nitric acid and hydrofluoric acid. Also, it can be weakened by alkaline oxidizing melts like potassium nitrate or sodium hydroxide. Tungsten is very resistant to corrosion but will combine with oxygen readily at very high temperatures to produce trioxides. Naturally, the metal is a mixture of 5 stable isotopes namely tungsten-180, tungsten-182, tungsten-183, tungsten-184, and tungsten-186 which have a percentage composition of 0.12%, 26.5%, 14.3%, 30.6% and 28.4% respectively.
Tungsten Physical Properties
Tungsten in its purest form is a shiny white metal that can easily be processed. It does however contain traces of oxygen and carbon within its chemical composition and this makes it very brittle when put under tremendous stress and force.Tungsten is the heaviest known engineering metal and has a very high density (19.25 g/cm3). This is due to its dense crystal formation. It has a very high melting point of 3 140 ° C and a boiling point high at 5 700 °C. Tungsten has the lowest vapor pressure of all metals and has the highest elasticity modulus of all metals at 400 GPa. It also has a very low thermal expansion coefficient of 4.4×10-6mm °C which is about the same as that of borosilicate glass and this is why it is used for glass metal seals.Tungsten is also environmentally friendly and does not decompose or breakdown easily.